Are you tired of watching your hair thinning or seeing it disappear altogether? Alopecia, a condition that affects millions worldwide, can be a distressing experience. But fear not, for in this enlightening blog post, we’re about to embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of alopecia: its causes, its symptoms, and most importantly, how to cure it.
Whether you’re someone grappling with this hair loss condition or just curious to understand it better, we’ve got you covered. Our aim is to equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to regain your confidence and embrace a fuller head of hair. So, let’s dive in and discover the key to overcoming it once and for all.
What Is Alopecia
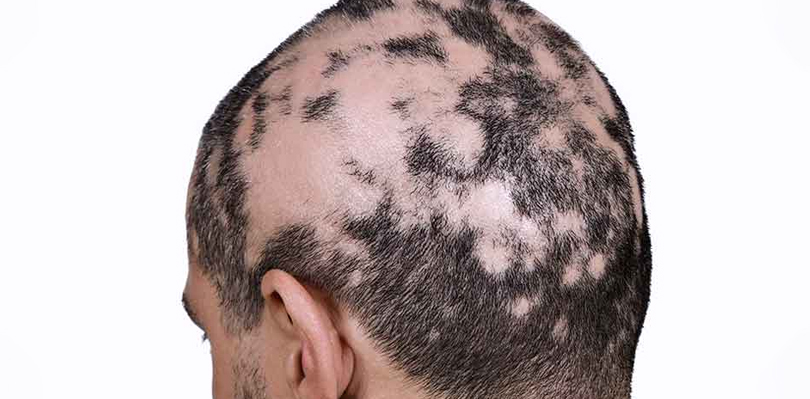
Alopecia is a medical term that encompasses a wide range of hair loss conditions, each characterized by the partial or complete loss of hair from various parts of the body, most commonly the scalp. It can affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, causing physical and emotional distress. It is often a result of the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
While the exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood, it is believed to be influenced by genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. It can manifest in various forms, such as areata, totalis, and universalis, each with its unique patterns of hair loss. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of it is crucial for effective management and treatment.
How To Cure Alopecia
Curing alopecia can be a complex and challenging process because it depends on the specific type and underlying causes of the condition. There is no one-size-fits-all cure for alopecia, but there are various treatment options available that can help manage and potentially reverse hair loss. Here are some steps to consider when addressing it:
Consult A Dermatologist Or Trichologist
Start by seeking professional medical advice. A dermatologist or Trichologist can accurately diagnose your specific type of alopecia and determine its underlying causes.
Identify The Underlying Cause
Understanding the root cause of it is crucial. It could be genetic, autoimmune (such as alopecia areata), hormonal, or related to other health conditions. Proper diagnosis will guide your treatment plan.
Medical Treatments
Depending on the type and severity of alopecia, your doctor may recommend various medical treatments, including:
Topical Medications
Minoxidil is a commonly prescribed topical medication for androgenetic alopecia (male/female pattern baldness).
- Corticosteroids:
These anti-inflammatory drugs may be used for conditions like alopecia areata.
- Immunotherapy:
For severe alopecia areata cases, drugs that modulate the immune response may be considered.
- Hormone Therapy:
In cases of hormonal imbalances contributing to hair loss, hormone therapy may be necessary.
Hair Growth Therapies
Some individuals opt for hair growth therapies like low-level laser therapy (LLLT), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, or hair transplant surgery. These treatments can stimulate hair follicles and promote regrowth.
Manage Stress
High levels of stress can exacerbate hair loss. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises may help.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintain a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins (especially biotin and vitamin D), minerals, and proteins. Stay hydrated, exercise regularly, and get sufficient sleep, as these factors can impact hair health.
Avoid Harsh Hair Practices
Refrain from using harsh chemicals, excessive heat styling, or tight hairstyles that can further damage the hair shaft and follicles.
Support Groups And Counseling
Dealing with hair loss can be emotionally challenging. Consider joining support groups or seeking counseling to cope with the psychological impact of alopecia.
Regular Follow-Ups
Continue to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Patience And Persistence
Keep in mind that hair regrowth can be a slow process, and results may vary from person to person. Be patient and persistent in following your treatment plan.
It’s essential to remember that while some individuals may experience complete regrowth of hair, others may achieve only partial improvement. The effectiveness of treatments can vary, so consult with your healthcare professional to determine the most suitable approach for your specific condition.
Alopecia Symptoms
Alopecia is a condition characterized by hair loss, and its symptoms can vary depending on the specific type of it a person is experiencing. Here are some alopecia symptoms:
Hair Thinning or Loss
The most obvious and common symptom of it is hair thinning or hair loss. It can occur gradually or suddenly, depending on the type of it. Small, round bald patches may appear on the scalp or other parts of the body.
Bald Patches (Alopecia Areata)
In cases of alopecia areata, which is an autoimmune condition, individuals often develop small, round, smooth bald patches on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or other hair-bearing areas of the body. These patches can vary in size and may come and go over time.
Changes In Nail Health (Alopecia Areata)
Some people with alopecia areata may notice changes in their nails, such as pitting (small dents or depressions), ridges, or white spots. These nail changes can be associated with the autoimmune nature of the condition.
Complete Hair Loss (Alopecia Totalis and Universalis)
Alopecia totalis involves the complete loss of hair on the scalp, while alopecia universalis extends to the loss of hair on the entire body, including eyebrows and eyelashes. These forms of it result in total hairlessness in affected individuals.
Itching Or Tingling Sensations (Alopecia Areata)
Some people with alopecia areata report sensations of itching, burning, or tingling in the affected areas before hair loss occurs. These sensations are often mild but can be uncomfortable.
Regrowth Of White Or Gray Hair (Alopecia Areata)
In cases of alopecia areata, it’s not uncommon for white or gray hair to regrow in the bald patches. This regrowth can contrast with the person’s natural hair color, creating a distinct appearance.
It’s important to note that it is a highly variable condition, and the severity of symptoms can differ from person to person. Additionally, the underlying causes and progression of it can vary widely, leading to different clinical presentations. If you suspect you have it or are experiencing unusual hair loss, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation and diagnosis from a dermatologist or healthcare professional. They can determine the specific type of it and recommend appropriate treatments or management strategies based on your individual circumstances.
Causes Of Alopecia
Alopecia, or hair loss, can result from various underlying causes. Here are a few common causes of it:
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male And Female Pattern Baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common cause of hair loss, affecting both men and women. It is primarily genetic and related to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT). In individuals genetically predisposed to this condition, DHT shrinks hair follicles over time, leading to thinner and shorter hair until eventually, no new hair growth occurs.
Alopecia Areata (Autoimmune Disorder)
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It often presents well-defined, round bald patches on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or other body hair. The exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood but is believed to involve genetic and environmental factors.
Telogen Effluvium (Stress Or Medical Condition)
Telogen effluvium is a temporary hair loss condition often triggered by severe stress, illness, surgery, or hormonal changes. It disrupts the normal hair growth cycle, causing a larger proportion of hair follicles to enter the resting (telogen) phase and subsequently fall out. Hair typically regrows once the underlying cause is addressed.
Alopecia Totalis And Universalis (Severe Forms Of Alopecia Areata)
These rare and severe forms of alopecia areata involve the complete loss of hair on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or the entire body, including eyebrows and eyelashes (alopecia universalis). Like areata, the exact cause is thought to be autoimmune, but it results in extensive and often permanent hair loss.
Medical Treatments And Medications
Some medical treatments and medications can cause hair loss as a side effect. Chemotherapy drugs, for example, are well-known culprits. Additionally, medications like anticoagulants, antidepressants, and certain blood pressure medications may lead to hair thinning or loss. Hair typically regrows once the medication is discontinued, but the extent of regrowth can vary.
It’s important to note that the specific cause of alopecia can vary among individuals, and sometimes multiple factors may contribute to hair loss simultaneously. Accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional or dermatologist is crucial to determine the underlying cause and tailor appropriate treatment or management strategies to address the individual’s unique circumstances.
What Experts Say About Alopecia
Experts agree that alopecia, a condition characterized by hair loss, can be complex and multifactorial. Dermatologists, trichologists, and medical professionals emphasize the importance of accurate diagnosis to determine the specific type and underlying cause of it. They stress that treatment approaches vary depending on the diagnosis, ranging from topical medications and hair growth therapies to addressing underlying medical conditions.
Experts also emphasize that early intervention often leads to more successful outcomes. Additionally, they highlight the need for ongoing research to better understand the causes and develop more effective treatments for the various forms of it, aiming to improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
FAQ
Can alopecia be permanently cured, or is it a lifelong condition?
The potential for a permanent cure for it depends on the type and underlying cause. For some individuals with androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness), permanent hair restoration can be achieved through treatments like hair transplant surgery. However, conditions like alopecia areata can be more unpredictable. While some people experience spontaneous hair regrowth, others may have recurrent episodes of hair loss. It’s crucial to consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for a personalized assessment and treatment plan based on your specific type of it.
Are there natural remedies or lifestyle changes that can help with alopecia?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes and natural remedies can complement medical treatments for it. These include maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients like biotin, vitamins, and minerals. Managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation and yoga can also help. Additionally, avoiding harsh hair practices, such as excessive heat styling or tight hairstyles, can prevent further hair damage. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan, as natural remedies alone may not be sufficient to address alopecia effectively.
Is there any hope for individuals with severe forms of alopecia, such as alopecia universalis?
While severe forms of it, like alopecia universalis, can be challenging to treat, there is hope. Some individuals with these conditions have experienced partial or full regrowth of hair through treatments like immunotherapy or other medical interventions. Research into new treatments and therapies for severe alopecia continues, offering potential options for improved outcomes. It’s essential for individuals with these conditions to consult with dermatologists or specialists who can provide the latest information on available treatments and research advancements to explore the best options for their specific case.

